Advanced Education
Privilege, agency, and the climate scientist’s role in the global warming debate
Background
One of the biggest surprises I found upon my return to the University of Victoria after spending 7 1/2 years in the BC Legislature was the overall increase in underlying climate anxiety being experienced by students in my classes. I’ve been teaching at the university level since the mid 1980s and for most of this time, the students in my classes considered global warming to be an esoteric and highly uncertain future threat. While some would express concerns about the growing concentrations of atmospheric greenhouse gases, very few understood, or even cared, how climate change could hypothetically affect them. It was always a problem that others, somewhere else in the world, might have to deal with sometime down the road – but not any more. My experience with this new generation of undergraduates is that they are both very aware of, and deeply troubled by, the threat of global warming. I am beginning to detect a sense of hopelessness and despair within growing numbers of youth. And this troubles me immensely.
For many years I, and my climate science colleagues around the world, spoke truth to power as we continually raised concerns about the ongoing consequences of dumping millions of tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere every year. But our warnings fell on deaf ears, or at least ears damaged by the never ending stream of spin, obfuscation and rhetoric being offered up by lobbyists, vested interests, charlatans and others desperate to maintain the fossil-fuel status quo. Yet those days are gone. So much has changed.
Perhaps the most notable increase in public awareness can be attributed to Greta Thunberg and her Skolstrejk för klimatet (School strike for climate). Starting from her lone Friday demonstrations on the steps of the Swedish parliament in August 2018, her movement quickly gained international attention leading to locally-organized Fridays for Future demonstrations around the world (see Figure 1 for images from a Friday, September 19, 2019 demonstration on the lawn of the BC Legislature).
Figure 1 : Four images taken on Friday, September 20, 2019 at a Global Week for Future demonstration on the lawn of the BC Legislature.
At the same time, extreme weather and climate extremes are seemingly becoming the norm rather than the anomaly, with hardly a day going by without a weather disaster somewhere in the world headlining the nightly news. And while in the past, these extreme weather events may have seemed to be someone else’s problem living elsewhere in the world, today no one is immune. Even meteorological terms like “heat domes”, “atmospheric rivers” or the “polar vortex” are becoming commonly used in casual conversation.
The cumulative efforts of so many over so many years in pointing out the importance of curtailing greenhouse gas emissions is finally paying off. Public awareness and desire for action is no longer a barrier to advancing climate policy. For example, one Pew Centre global survey spanning 17 countries in Europe, the Asia-Pacific, and North America indicated that 80% of people surveyed were “willing to make [a lot of or some] changes about how [they] live and work to help reduce the effects of global climate change” (Bell et al., 2021). The greatest barrier, in my view, remains political will. Too many of our elected representatives end up treating politics as a lifelong career instead of a sense of civic duty wherein you step in for a few years, do your part, then step out and let others take over. After a while, one might cynically expect such career politicians to naturally start focusing more on populist and short term policy measures that can successfully be developed and implemented prior to the next election. It would allow that politician to identify short term successes as direct evidence that they were delivering results for their constituents.
By its very nature, climate policy requires a much longer term perspective to be taken. It requires recognition that today’s decision-makers wont have to live the consequences of the climate-related decisions (or lack thereof) that they make. Yet I have always believed that global warming represents the greatest opportunity for innovation, creativity and economic prosperity the world has ever seen since every environmental challenge can also be viewed as an opportunity for innovation and creativity as we seek to address the underlying challenge. Instead of dwelling on the scale of the challenge and hence its apparent hopelessness, which only feeds an individual’s climate anxiety, it can be incredibly empowering to pivot to a focus on developing climate solutions. And herein lies an opportunity for the climate science community.
Climate Anxiety
Climate anxiety is a very real psychological and emotional response to concern about uncertain future climate change impacts (American Psychological Association, 2017, Doherty and Clayton, 2011). Defined as a chronic fear of climate or environmental doom, an individual’s chronic climate anxiety is magnified by extreme weather and climate events that have been experienced personally and/or by those in their close networks.
For example, climate anxiety in North America increased in the summer of 2021 because of intense, record-breaking heatwaves and wildfires (Bratu et al., 2022). As well, increased climate anxiety was almost certainly triggered in those who experienced September 2022’s widespread destruction caused by Hurricane Fiona and Ian’s historic winds, wave activity and storm surge.
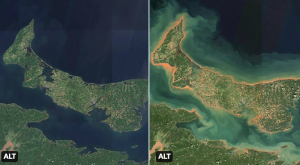 Figure 2: Canadian Space Agency satellite images taken on August 21, 2022 (left) and September 25, 2022 (right). Extensive coastal erosion of Prince Edward Island was caused by historic storm surge and wave activity associated with Hurricane Fiona.
Figure 2: Canadian Space Agency satellite images taken on August 21, 2022 (left) and September 25, 2022 (right). Extensive coastal erosion of Prince Edward Island was caused by historic storm surge and wave activity associated with Hurricane Fiona.
Climate scientists are not immune to climate anxiety. Many within our community have felt compelled to speak out publicly regarding the causes, consequences, and seriousness of global warming. Others have signed petitions, penned letters, written books and commented on social media sites. However, few have actively sought election to government office. This is unfortunate as I continue to believe that political will remains the greatest barrier to advancing climate policy including the decarbonization of global energy systems. But instead of helping to generate that political will, a large cohort of the climate science community, in an attempt to deal with their own climate grief, has heightened rather than alleviated climate anxiety in civil society.
Through this article, I hope to encourage that community to reflect upon the privilege and agency they have to refocus and mobilize their efforts towards advancing climate solutions within society, and to appeal to their sense of civic duty to inspire more to seek elected office. In particular, I argue that:
- Inaccurate scientific messaging associated with the 2018 IPCC Global Warming of 1.5°C report is feeding climate anxiety, and this is leading to despair in youth.
- There are more effective ways for scientists, armed with privilege and agency, to advocate for climate policy than fear-based messaging and civil disobedience.
As Albert Einstein famously noted: “Those who have the privilege to know have the duty to act, and in that action are the seeds of new knowledge.” After reading the rest of this blog, I hope you agree that this quote could be expanded with an additional sentence. “And as the new knowledge grows, the solutions to global warming are revealed.”
Scientific messaging is feeding climate anxiety
The 2018 IPCC Special Report outlining greenhouse gas emission pathways to limit warming to 1.5°C above preindustrial levels (IPCC, 2018) almost certainly contributed to an escalation of overall climate anxiety in recent years. The Special Report was a response to an invitation from signatories to the UNFCC as part of the Paris Agreement. The 2015 Paris Agreement, joined by 193 member states, has the specific goal of:
Holding the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, recognizing that this would significantly reduce the risks and impacts of climate change (UNFCC 2015).
The aspirational 1.5°C target was added in response to lobbying by small island states (and their allies).
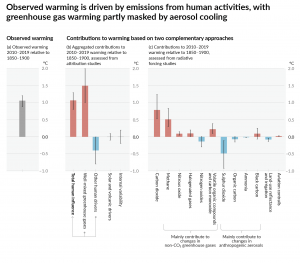
While the scientific community responded by outlining pathways to mitigate warming to 1.5°C in (IPCC, 2018), the subtleties embedded within the report seem to have been lost in its dissemination to the public. It is well known that the world has already warmed by 1.2°C since preindustrial times, and if we immediately eliminated all fossil fuel combustion worldwide, we would warm by an additional 0.5°C (IPCC 2021; see Figure 2) as the direct and indirect cooling global effects of aerosols (also associated with fossil fuel combustion) dissipate through gravitational settling and precipitation scavenging. The Earth would warm further as we equilibrate to the present 508 PPM CO2e (NOAA 2022) greenhouse gas loading in the atmosphere, and that is not counting the permafrost carbon feedback which could add another 0.1° to 0.2°C this century to committed warming (Macdougall et al, 2013).
In other words, meeting the 1.5°C target requires an immediate global scale up of negative emissions using technologies that have yet to be developed. Given socioeconomic inertia in our built environment (Matthews and Weaver, 2010), the scale of negative emissions required, and the preponderance of more urgent political priorities (i.e. healthcare, housing, inflation, the economy, the war in Ukraine and so forth), it is not possible for the world to meet the 1.5°C target.
Figure 3: Observed global warming (2010-2019 relative to 1850-1900) and the contribution to this net warming by observed changes to natural and anthropogenic radiative forcing. Reproduced from IPCC (2021).
 Climate anxiety is also fueled by media messaging related to the perception of a looming climate ‘crisis’ (Crandon et al., 2022). Take the anxiety effect of popular messaging related to the aspirational goal of remaining below a 1.5°C global warming threshold (IPCC, 2018). “We have only 12 years left to limit climate change catastrophe, warns UN” was the headline of a story published in the Guardian on October 8, 2018; “Only 11 years left to prevent irreversible damage from climate change, speakers warn during general assembly high-level meeting” was the headline of a press release issued by the United Nations on March 28, 2019 during its 73rd session (UN, 2019); “Climate change: 12 years to save the planet? Make that 18 months” was the headline of a BBC News story on July 24, 2019 (BBC, 2019).
Climate anxiety is also fueled by media messaging related to the perception of a looming climate ‘crisis’ (Crandon et al., 2022). Take the anxiety effect of popular messaging related to the aspirational goal of remaining below a 1.5°C global warming threshold (IPCC, 2018). “We have only 12 years left to limit climate change catastrophe, warns UN” was the headline of a story published in the Guardian on October 8, 2018; “Only 11 years left to prevent irreversible damage from climate change, speakers warn during general assembly high-level meeting” was the headline of a press release issued by the United Nations on March 28, 2019 during its 73rd session (UN, 2019); “Climate change: 12 years to save the planet? Make that 18 months” was the headline of a BBC News story on July 24, 2019 (BBC, 2019).
 To amplify the urgency of further climate action, “Climate Clocks” were developed that purported to count down days until it was too late to avoid the worst impacts of global warming (see here and here). It is unclear how watching a countdown to catastrophe would do anything other than increase climate anxiety and instill a sense of hopelessness and despair. Political rhetoric from those with large followings, such as when Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez proclaimed “The world is going to end in 12 years if we don’t address climate change” (USA Today, 2019), also contributes to increasing climate anxiety.
To amplify the urgency of further climate action, “Climate Clocks” were developed that purported to count down days until it was too late to avoid the worst impacts of global warming (see here and here). It is unclear how watching a countdown to catastrophe would do anything other than increase climate anxiety and instill a sense of hopelessness and despair. Political rhetoric from those with large followings, such as when Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez proclaimed “The world is going to end in 12 years if we don’t address climate change” (USA Today, 2019), also contributes to increasing climate anxiety.
![]() Inherent in the 12 years left narrative, and the IPCC 1.5°C report is the implied notion that there is something magical about the number 1.5°C. Of course, there is no scientific rationale to justify an acceptable warming threshold of 1.5°C instead of 1.3°C or 1.672°C. Any defined level of ‘acceptable’ warming obviously involves an assessment of societal values and those will clearly be different depending on where you live in the world.
Inherent in the 12 years left narrative, and the IPCC 1.5°C report is the implied notion that there is something magical about the number 1.5°C. Of course, there is no scientific rationale to justify an acceptable warming threshold of 1.5°C instead of 1.3°C or 1.672°C. Any defined level of ‘acceptable’ warming obviously involves an assessment of societal values and those will clearly be different depending on where you live in the world.
In fact, even the 2°C threshold for acceptable warming originally only entered the public arena shortly after the IPCC released its Second Assessment Report and prior to the establishment of the Kyoto Protocol. In 1996, the Council of the European Union concluded:
The Council recognizes that, according to the IPCC S.A.R., stabilization of atmospheric concentrations of CO2 at twice the pre-industrial level, i.e. 550 ppm, will eventually require global emissions to be less than 50% of current levels of emissions; such a concentration level is likely to lead to an increase of the global average temperature of around 2°C above the pre-industrial level.
And:
Given the serious risk of such an increase and particularly the very high rate of change, the Council believes that global average temperatures should not exceed 2 degrees above pre-industrial level and that therefore concentration levels lower than 550 ppm CO2 [carbon dioxide] should guide global limitation and reduction efforts. This means that the concentrations of all greenhouse gases should also be stabilized. This is likely to require a reduction of emissions of greenhouse gases other than CO2 in particular CH4 [methane] and NO2 [sic; nitrous oxide].
Ironically, it was inconsistent on the one hand, for the EU Council to advocate for carbon dioxide to be stabilized at or below 550 ppm with emissions eventually dropping to less than 50% of 1996 levels, while on the other hand, arguing for the 2°C threshold not to be exceeded.
While ambitious goal-setting can in theory be an effective motivator of action (Locke and Latham, 2002), in practice, alarmist media reframing (Ereaut and Segnit, 2006) of failure to remain below the 1.5°C goal into a scenario of impending doom has become quintessential fuel for personal climate anxiety. Taken in the collective across society, climate anxiety driven by personal concern and amplified by poorly calibrated media messaging is quickly emerging as a dominant factor in the collective zeitgeist of the Anthropocene (e.g. Crutzen 2006, Hickman et al 2021, Wray 2022).
Given that most of today’s decision-makers will not be around to be held accountable for their action, or lack thereof, towards meeting various targets set well into the future, a more appropriate framing and scientifically justifiable statement is for society to collectively do what we can to avoid as much warming as possible. Every tenth of a degree warming avoided reduces our collective climate risk and, by corollary, our overall collective climate anxiety.
But this still doesn’t address how individual climate anxiety can be reduced.
A far more constructive approach would be for the scientific community to turn our collective attention to climate solutions, not climate fear mongering or climate alarmism. Take the recent viral Tik Tok video showing Nasa Scientist Dr. Peter Kalmus prior to getting arrested after chaining himself to a JP Morgan Chase building in Los Angeles. The emotion in Dr. Kalmus’ voice indicates that he is likely dealing with his own climate anxiety, but I question whether or not the message in his viral video did anything more than increase the level of anxiety within children and youth worldwide:
“So, I am here because scientists are not being listened to. I am willing to take a risk for this gorgeous planet. That sucks, and we’ve been trying to warn you guys for so many decades now we are heading towards a catastrophe. And we are being ignored, the scientists of this world are being ignored, and it’s got to stop. We are going to lose everything, and we are not joking. We are not lying; we are not exaggerating. This is so bad everyone that we are willing to take this risk and more and more scientists, and more and more people are going to be joining us. This is for all the kids of the world — all of the young people, all of the future people. This is so much bigger than any of us. It’s time for all of us to stand up and take risks and make sacrifices for this beautiful planet that gives us life.”
At no point were any solutions posed, any positive actions suggested, or any personal climate risk reduction advocated for. The scientists involved likely believed that they were raising public awareness of the seriousness of global warming. Yet I argue that these same scientists abdicated their position of power and privilege by inadvertently pretending to be on the same footing as those most affected by climate change. In doing do, the scientists did little more than stoke the fires of climate anxiety when they had agency to facilitate constructive change both within their public engagements, as well as their own personal choices.
It’s also long been known that fear based messaging does not work in terms of motivating personal climate action (e.g., O’Neill and Cole (2009) , Stern (2012), Climate Tracker (2017). In fact, many simply disassociate themselves from the issue. Others, of course, take the fear to heart and it feeds their underlying climate anxiety.
Articles like McKay et al., 2022, with provocative, if not highly speculative, titles may attract media attention in the lead up to an annual UNFCCC COP event. But they are often framed as opinion or expert assessment and so are often highly controversial and not representative of broad scientific consensus. Extremely low probability, perhaps even impossible, but certainly poorly understood tipping point scenarios often end up being misinterpreted as likely and imminent climate events. The nuances of scientific uncertainty, the differences between hypothesis posing vs hypothesis testing, and the proverbial “implications of this work” throw away statements, wherein scientists take creative license with speculative possibilities, are all lost on the lay reader as the study goes viral across social media.
More recently, some activists have even called on the scientific community to engage in more civil disobedience (e.g., Capstick et al., 2022, Earth.org, 2022) arguing that it is effective and leads to change. Once more, I am not sure how activist scientists with agency help advance the necessary solutions and believe that the time for such activism has long passed. Governments around the world have committed to climate action but are struggling to advance the various solutions required for the low carbon economies of tomorrow. They need help, ideas, solutions and ongoing support and the scientific community is ideally positioned to assist in this regard.
In fact, many look to the climate science community for leadership on greenhouse gas mitigation and do so with dismay when they see these same scientists jetting off to various conferences, UNFCCC COP/IPCC meetings and workshops at exotic locations around the world. How many thousands of people attended the 26th Conference of Parties meeting of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Glasgow in 2021? How many attended the 27th meeting in Sharm el-Sheikh in 2022? Was their presence really necessary? Climate scientists, with their privilege and agency, not only have a responsibility to assist identifying and implementing climate solutions; they also need to model the climate leadership they are calling on others to follow. Failing to do so sends the wrong message, a message that undermines the prevailing narrative that we are in a “climate emergency”.
More effective ways for scientists to advocate for climate policy
The climate science community operates from a position of privilege in the public discourse of climate change science, its impacts and solutions. Whether it be by participating in the writing of IPCC reports or our own research, climate scientists have defined the scale of the global warming challenge, outlined pathways to decarbonization of our energy systems, and documented a suite of future impacts, many of which would be very detrimental to future societies. We’ve also quantified the climate risk to our natural and built environment. Armed with this knowledge, climate scientists, more than most, are well-informed and so have agency in the advancement of climate solutions. But when climate scientists participate in civil disobedience or do little more than criticize others for inaction, they abdicate that position of privilege and agency by pretending to be on the same footing as others in society who are not as well informed on the nuances of climate change. As such, rather than alleviating their own, and broader society’s, climate anxiety, they fuel it further by inadvertently ratcheting up the rhetoric with nothing to offer in terms of overall solutions or risk reduction. I firmly believe that the climate science community has a duty and responsibility to become more actively engaged in the delivery of climate solutions in whatever form they feel most comfortable work with (i.e., nature-based, technological, socioeconomic or policy solutions).
At the same time, the scientific community must be reminded that they are but one stakeholder in the global warming debate. Whether or not society wishes to respond to the challenge of global warming really boils down to one question. Do we the present generation owe anything to future generations in terms of the quality of the environment we leave behind? Yes or No? Science cannot answer this question; but it can help articulate the expected consequences of action or inaction. Science can also inform decision makers by pointing out that if the answer to the above question is yes, dramatic GHG reductions (both through the decarbonization of energy systems and the introduction of negative emission technology) must commence now. Waiting until the future to start reducing emissions means waiting until it is too late.
While the answer to the above question is fundamentally personal, most almost certainly would respond yes, particularly those who have children. Yet some would disagree. For example, “Some evangelicals argue that global warming is of little concern when the end times are approaching. Indeed, it could even be proof of it” (Gander, 2019); Fatalists may believe that what will occur in the future is inevitable, perhaps even a manifestation of God’s will, and so believe that an individual’s actions or choices will have no effect on the direction we are heading. Libertarians may focus on the importance of individual freedoms, express concern about government overreach and regulation and may advocate for a laissez-faire approach to climate policy. There might be some who might answer yes to question, but their deep suspicion of environmentalists may make them question the urgency of dealing with global warming. Then of course there are those who will have been swept up in the various conspiracy theories so prevalent on the internet these days. Fortunately, the Pew survey cited above (Bell et al., 2021) allows us to estimate that it is only about 20% of the population who will likely object to the advancement of climate policy. And so, I am of the firm belief that engaging with this audience is counter-productive and a waste of a climate scientist’s time.
Instead of trying to persuade the unpersuadable, participating in civil disobedience or publicly demanding government take unspecified actions it would be far more productive if the scientific community, turned their attention to the development and advancement of climate solutions. This can be accomplished in any one of a number of ways. For example:
- Supporting progressive government policy vocally and publicly once it has been introduced;
- Running for office;
- Advocating for constructive solutions in recognition that we have agency and we occupy a position of privilege in society.
Given the emergence of social media in this post-truth age we are seeing more and more populist policies globally wherein decisions are made first, and then evidence (real or imagined) is sought after the fact to support an ideological agenda — this is what I call decision-based evidence-making, the antithesis to the scientific method. Scientists are driven by the quest to understand the world around us. We are driven by evidence. We identify problems and then take steps to solve these problems using reproducible techniques. Central to who we are as scientists is the notion of evidence-based decision-making. We understand this notion and react strongly to decision-based evidence-making, the antithesis to the scientific method. I truly believe our community has an inherent responsibility to exhibit the necessary leadership (especially through our own behaviour) to ensure that we play a constructive role in identifying solutions to the environemental problem that we have spent so many decades studying.
Finally, a co-benefit our community will warmly welcome in the move towards a climate-solutions focus, is the amelioration of our own climate anxiety (not to mention broader societal climate anxiety). I say this from personal experience, having worked in the field since the 1980s. Climate scientists, like others in the general public, often also struggle with the notion of climate anxiety and grief. But unlike others in the general public, our community holds agency and a position of privilege in the global warming debate. Rather than denying this agency and privilege I am hopeful that as a community we will collectively rise to the myriad opportunities global warming has afforded us for constructive public engagement and the betterment of society.
In the weeks ahead, I hope to expand upon these initial ideas by offering more concrete examples of engagement and responding to any feedback coming my way from this post.
Progress towards creating 2900 new tech-related spaces in postsecondary institutions
Budget estimate debates for the Ministry of Advanced Education were held yesterday. I took the opportunity to ask the Minister about government’s progress towards creating the promised 2,900 additional tech-related spaces in public post-secondary institutions. This was supposed to result in 1,000 additional grads per year by 2023.
Below I reproduce the text and video of the exchange. As you will see from the response, I am pleased that the government appears to be on track to reach this target.
Video of Exchange
Text of Exchange
A. Weaver: Thank you. I appreciate that.
The next question is with respect to the government announcements regarding the tech industry and the 2,900 additional tech-related spaces that the minister announced would be made available through public post-secondary institutions. This was supposed to result in 1,000 additional grads per year by 2023. Start-up funding was $4.4 million last year, but was expected to increase to $42 million.
I have two questions on this particular aspect. Is this plan still on track, number one? Two, how many spaces were added at B.C. post-secondary institutions last year?
Hon. M. Mark: Yes, the plan is on track. We began with 380 full-time-equivalent student spaces. We have a multi-year plan, to the member’s question. It started with an investment, as he noted, of $4.4 million to post-secondary institutions in 2017-2018. It increased to a total of $7 million in 2018-2019, and it continues to increase over the course of the new three-year fiscal plan. In 2019-2020, we plan to provide $24.9 million in funding, with further increases to come in subsequent years.
A. Weaver: Thank you to the minister for the answer. According to the CEO of the B.C. Tech Association, access to talent is the single greatest barrier to growth for B.C. tech companies and the industry as a whole. In fact, it’s got to such a state in British Columbia that there are companies acquiring other companies solely for the talent that the company actually holds.
I’m wondering whether or not government believes that the investments they’re making are adequate — what metrics are they using to determine whether or not they are adequate? — and whether or not they believe their goals are being reached.
Hon. M. Mark: I want to acknowledge the work of B.C. Tech. We’ve got the third annual tech summit coming up next week. We’ve got a huge delegation of young people that are going to come from across the province to participate in that forum.
It’s a continuation of previous work that was done by the former government. But we’re talking about three years. So when the member asks, “is this significant…?” It’s a start; 2,900 seats is a lot for this system. It’s the first lift in a decade.
We’re very, very proud of that. We also have to look at the system and their capacity — the availability of facilities, equipment and instructors. So we will continue to invest in tech spaces, and we’re going to continue to work with industry. For right now, we’re just very proud of this first step. There will be more.
When will BC get a needs-based grant system for postsecondary education?
Budget estimate debates for the Ministry of Advanced Education were held yesterday. I took the opportunity to ask the Minister whether she was considering reintroducing a needs-based grant system for postsecondary students and, if so, when?
Below I reproduce the text and video of the exchange. As you will see from the response, I am cautiously optimistic that we will be heading in this direction.
Video of Exchange
Text of Exchange
A. Weaver: I have a number of questions. To speed the process up, we’ve delivered them through to the minister’s office in advance. Hopefully, we’ll be able to get through these in a timely fashion.
My first question is with respect to student loans and need-based assessment. We are, as the Chair will know, the only province in Canada without a form of a needs-based grant system for post-secondary students. We used to have one in British Columbia. In 2004, it was eliminated.
My question is: is the minister considering reintroducing a needs-based grant system and, if so, when?
Hon. M. Mark: Chair, I thank you for the question from the member opposite.
We are committed to making post-secondary education training more accessible and affordable. Every year we provide approximately $56 million to students to reduce funding barriers and improve access and affordability. Of this amount, approximately $32.3 million will go to over 20,000 students to reduce B.C. student loan debt in 2018-2019.
We also provide targeted debt reduction to students completing programs for certain in-demand occupations — to medical and child services professionals working in underserved communities — as well as to students with disabilities.
But there is more to do. Students are telling me that the upfront costs of a post-secondary education are also a barrier. We want to ensure that we have the right mix of financial supports in place to help students be successful. The previous government had 16 years to shape the student financial aid system in British Columbia and introduced a number of new programs while discontinuing a number of others, including replacing the previous needs-based access grant with the loan reduction program.
I’ve asked my team to take a close look at the full range of financial supports we provide to ensure the right supports get to the right students at the right time. We will not leave British Columbians behind.
I thank the member opposite for the question.
A. Weaver: I appreciate the answer. I’m just wondering if we can potentially get a yes or no on that. Is the minister considering a needs-based grant system or not? I appreciate the other information she gave, but the question was quite specific as to whether a needs-based grant is expected to be introduced in the province of British Columbia. We are the only province in the country of Canada to not have such a system in place.
Hon. M. Mark: We are considering it, but we’re doing the policy work. There is a saying: fail to plan, plan to fail. We’re reviewing the number of resources available to students. We want to hit the right target.
Implementation of sexualized violence & misconduct policies at BC postsecondary institutions
Budget estimate debates for the Ministry of Advanced Education were held on March 7. I took the opportunity to ask the Minister about the status of government’s review of progress made at British Columbia postsecondary institutions towards the implementation of sexualized violence & misconduct policies.
Below I reproduce the text and video of the exchange. As you will see from the response, government has established a working group comprising of students, institution staff and a community organization resource was convened in December 2018.
The working group reviewed the feedback received and provided input to the development of a draft action plan for the minister’s consideration. Review of institution policies was an area considered by the working group.
Video of Exchange
Text of Exchange
A. Weaver: Thank you to the minister for the answer. My final area for canvassing is with respect to the Sexual Violence and Misconduct Policy Act that was brought in under the previous government. Under the act, the minister can direct a post-secondary institution to conduct a survey or to review its sexual misconduct policy in order to determine its effectiveness.
We’re aware that a survey was actually done on the effectiveness of this legislation and post-secondary policies. So my question is…. I’ve a number of questions here. Are there plans for a more substantial review of these policies in the future, and if yes, what is the timeline for that?
Hon. M. Mark: I thank the member opposite for the question. I first want to acknowledge his advocacy. I want to acknowledge the former government’s efforts to put a law into place. I want to acknowledge that these steps will lead, hopefully, to better safety and outcomes for people.
Most of the institutions formalized their policies in 2017, and the legislation requires institutions to review their policies every three years, whether the minister directs it or not. Most institutions will be undertaking reviews prior to May 2020. These reviews are required to include student consultation. Institutions are responsible for the review of their policies in determining what amendments or additions may be needed to best meet the needs of their students and campuses.
Further to the survey that was undertaken by the ministry as part of an outreach engagement campaign in the winter of 2017-2018 after we formed government, a working group comprised of students, institution staff and a community organization resource was convened in December 2018.
The working group reviewed the feedback received and provided input to the development of a draft action plan for the minister’s consideration. Review of institution policies was an area considered by the working group. We will be working closely with the institutions over the next several months to further explore next steps.
I can assure the member opposite that recommendations are being drafted as we speak. I’m anxiously awaiting what the students and the working group has had to say. We as a government are committed to moving forward to ensure that we address student safety on campus.
The Chair: Member, and noting the hour.
A. Weaver: I must note the hour, hon. Chair. I would suggest that, perhaps, it is appropriate for the minister to note said hour, and I’ll take my place and allow it.
The Chair: Go ahead with your question. Just that this will likely be the last question.
A. Weaver: I will make a comment. I appreciate the answer from the minister. Of course, different institutions have a different capacity to actually introduce and enable these sexualized violence and misconduct policies. Some institutions have been more successful than others.
We have also undertaken an attempt to receive feedback from various institutions across the province, particularly of student groups. There is differing and varied implementation, and I certainly look forward to the recommendations coming forward from that group, because there is a lot of work that needs to be done.
Of course, as the minister will know, institutions do not want sexualized violence issues to be public because institutions want to be branded safe institutions for their student body. There’s an inherent desire to keep this under the radar, so to speak, and one of the purposes of introducing the policy measures last time was to ensure that institutions grapple with the very real problem that’s ongoing. I look forward to the results.
In September, the ministry began an information campaign. This campaign featured posters that implied that rape culture is wrong. These posters, however, were not very informative. Students need information about the supports that are available to them.
I had a series of questions here. I can just toss them all out at the same time, because the minister should’ve received these in advance. Who did the ministry consult in the design of these posters? Will this information campaign be continuing next year? Will there be a substantive review of the effectiveness of this campaign? How will the ministry incorporate support resource information into the posts going forward?
Hon. M. Mark: Again, thank you for raising the important issue. If we’re talking about making systemic change, we have a law. The law led to policies. The policies, when I came on as minister, were found on some websites — if you had a password or not. I’m not trying to be critical, but I didn’t think it was good enough to have policies on a website that means nothing to students.
We wanted to reach out to students who told me as minister, when I visited all of the campuses, that this was a serious issue. And it’s one that takes great courage for people to come forward to say: “I’ve been a victim.”
Regardless of who you are, I’m not telling you what the face is. That was the point of the campaign. The campaign was: we don’t know what that face is, and let’s not generalize. Let’s not stereotype that it’s a guy or girl.
Part of the idea of Tinder…. I’m not familiar with Tinder; I’m married, for those of you watching at home. Tinder — you know, swipe right, swipe left. That was the idea. The idea was to try to capture a younger audience. I’m not 22. I’m not going to university anymore, where we know that young people are on their phones. And we wanted a campaign that was going to be somewhat provocative.
I heard from students, who said: “Hey, we weren’t really expecting this from the minister.” It was a step and a strategy that we’re doing. We have a working group that is giving us as a ministry a lot of suggestions and recommendations and advice on what we should do to address this very, very serious issue. But when it comes time for the campaign…. The campaign was timed to meet the highest points of risk, the first two weeks of school. We launched the campaign again in January, with the highest points of risk in school.
I can’t answer your question about whether or not we will relaunch the same campaign. I’m taking direction advice from the students who have taken their time to tell me how we should address this systemic issue. There will be more to come, but that was, in essence, the premise of how we came up with the campaign. Was it enough? We wanted a campaign that could speak for itself. Part of it was to get people talking.
Noting the hour, I move that the committee rise, report completion of the resolution of the Ministry of Children and Family Development, report progress on the Ministry of Advanced Education, Skills and Training and ask leave to sit again.
UVic gets major boost in student housing
Today I had the honour of participating in an announcement at the University of Victoria outlining a major new investment in student housing via the BC Student Housing Loan Program. Two new buildings will be built on the campus to house 782 students (a net increase of 630 student homes). In addition, a new dining hall and multipurpose space will be incorporated into the new space. 
I’m thrilled to see this student housing project move forward at the University of Victoria. Not only will this new project provide critically needed on-campus housing, but the new buildings will also be constructed to the Passive House standard. Both UVic and the Province are demonstrating leadership in innovative low-carbon housing solutions, and I look forward to similar projects rolling out throughout British Columbia in the months ahead.
Today’s announcement is not only good for students, but also for individuals and families trying to rent across Greater Victoria. We have one of the lowest rental vacancy rates in the province, and because of a lack of on-campus housing, students are competing with everyone else in Victoria for the same scarce rental units. By better meeting the needs of students with on-campus housing, this project will help ease the pressure in the rental market.
Below is the text of the brief speech I gave at the event.
Text of Speech
 I’m delighted to be here today to welcome the news that UVic will see the construction of 782 new homes for students (of which 620 are net new).
I’m delighted to be here today to welcome the news that UVic will see the construction of 782 new homes for students (of which 620 are net new).
UVic students have been in desperate need of more affordable, on-campus housing for years now.
Ever since I was first elected as an MLA in 2013 I’ve been calling on government to take steps to create more student housing at UVic, as well as other universities across BC.
I’m thrilled that the BC NDP government is listening and making increased student housing a reality.
Today’s announcement is not only good for students, but also for individuals and families trying to rent across Greater Victoria.
As I’m sure everyone here knows, we have one of the lowest rental vacancy rates in the province.
And because of a lack of on-campus housing, students are competing with everyone else in Victoria for the same scarce rental units.
By better meeting the needs of students with on-campus housing, this project will help ease some of that pressure in the rental market.
It will free up rental units in the rest of the city for everyone else who is looking for a place to call home.
I find this project particularly exciting not only because it will provide critically-needed on-campus housing, but also because the new buildings will be constructed to the Passive House standard.
The Passive House standard is a world-leading standard for energy efficiency. This is exactly the type of innovative approach that we need to take in dealing with the climate crisis.
In every new building, in each new piece of infrastructure, we have an opportunity to reduce our emissions and build the type of communities we want.
UVic and the province are demonstrating leadership in developing innovative low-carbon housing solutions. In fact, every capital project government is involved in should be seen through the lens of low carbon innovation.
I offer my sincere thanks and congratulations to both UVic and the government of BC for demonstrating leadership in dealing with our affordability crisis while at the same time recognizing the opportunity for innovation in the low carbon 21st century economy.