Environment
Electing Strong Island Voices for a Strong Canada
Sunday, March 9, 2025, Dürres, Albania:
Mark Carney was just elected to lead the Liberals into the forthcoming Canadian federal election. This election is turning out to be one of the most important in Canadian history.
In Russia, Valdimir Putin continues his expansionist dreams of rebuilding the Soviet Union through his latest campaign of terror, violence and war crimes now aimed at the Ukrainian people. Meanwhile, in the middle east, Gaza lays in ruins, the Syrian government has been overthrown, and tensions continue between the Israeli government and the Iran-supported terror organizations Hamas, Hizballah, and the Houthis. In Europe, Germany’s far right Alternative for Germany (AfG) party made stunning gains in the 2025 election. Virtually every region of the country that was once under East German communist rule supported the anti-immigration AfD campaign. Meanwhile many parts of Africa and Asia continue to experience civil unrest.
Historically, the world would have turned to America and its NATO allies to broker peace and maintain world order. But all that has changed with the election of Donald Trump. He is waging trade wars against allied nations thereby undermining international trade and security agreements. He insults international leaders on an almost daily basis. Whether it be calling Prime Minister Justin Trudeau the Governor of the great state of Canada or acting like a school yard bully to publicly demean Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy, the man has no limit.
The chaos created by Donald Trump has caused the Dow Jones Industrial Average to tumble recently, completing a classic double-top trading pattern suggesting a major market correction is in the cards. His delusional dreams of rebuilding Gaza into a Mediterranean paradise, or annexing Greenland and Canada are all signs of a very disturbed man. Donald Trump is making America weak again.
 Donald Trump’s niece Mary Trump holds a PhD in clinical psychology from Adelphi University’s Derner Institute of Advanced Psychological Studies, the first university-based professional school of psychology in America. As a clinical psychologist and daughter of Donald Trump’s older brother Fred, she is uniquely qualified to comment on the president’s psychiatric condition. She didn’t hold back in her tell-all book Too Much and Never Enough: How My Family Created The World’s Most Dangerous Man.
Donald Trump’s niece Mary Trump holds a PhD in clinical psychology from Adelphi University’s Derner Institute of Advanced Psychological Studies, the first university-based professional school of psychology in America. As a clinical psychologist and daughter of Donald Trump’s older brother Fred, she is uniquely qualified to comment on the president’s psychiatric condition. She didn’t hold back in her tell-all book Too Much and Never Enough: How My Family Created The World’s Most Dangerous Man.
There she writes that he displays all nine characteristics of narcissistic personality disorder as detailed in the American Psychiatric Society’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. She further suggests that he may suffer from dependent personality disorder, antisocial personality disorder and “long undiagnosed learning disability that for decades has interfered with his ability to process information.” Perhaps this explains his behaviour, admiration of authoritarian demagogues and chaotic approach to governance.
But at the same time, it’s easy to manipulate such an individual by simply playing to their unabated, all-consuming egotism. And so, Trump has surrounded himself with sycophants, the brightest of whom know how to influence him to get exactly what they want.
For much of the spring term, I’ve been on sabbatical in Albania. It’s been a life changing experience as I’ve got to know the people and the country. Albania is a new democracy and much of the country has been rebuilt this century. Memories of persecution and terror under the communist dictatorship that ended in 1991 as well as the 1997 civil war are still fresh in people’s minds. Life is hard for many.
 Albania still has a few governance and infrastructure wrinkles to iron out prior its planned 2030 entry into the European Union. But the spring in the gait of the hardworking people, the joyous interactions I had with so many, and the generosity of those who had so little to give affected me deeply. It’s a society where people look out for one another.
Albania still has a few governance and infrastructure wrinkles to iron out prior its planned 2030 entry into the European Union. But the spring in the gait of the hardworking people, the joyous interactions I had with so many, and the generosity of those who had so little to give affected me deeply. It’s a society where people look out for one another.
While officially a secular state, more than half of Albanians are Muslim. The Muslim majority live in harmony with the Orthodox and Catholic minorities. Like France, Albania only recognizes civil unions and so its not uncommon to see muslims marry christians or orthodox wed catholics.
Yet while Albanians celebrate their freedom and newly found democracy, America is heading in the opposite direction. Even here in British Columbia, the BC NDP’s introduction of Bill 7 — Economic Stabilization (Tariff Response) Act signalled a disturbing trend towards more autocratic governance. Vancouver columnist Vaughn Palmer writes “In 41 years of covering B.C. governments, I’ve not seen a legislation as arbitrary and far-reaching this side of the federal War Measures Act.”
Since the inauguration of Trump, Canadian sovereignty has come under attack. Watching this from afar was very difficult. It’s critical that Canada has stabled principled leadership in these difficult times. And Mark Carney is exactly the type of person Canada needs. The Conservative Party appears to have been taken over by extreme elements whose behaviour mirrors that of the Republican Party south of the border. Those identifying with the progressive conservative roots of the Conservative Party have been left feeling alienated; the NDP do not have the leadership required to take on Donald Trump, and the Canadian Greens are disorganized and mired with never-ending infighting.

 But here’s the dilemma. On Vancouver Island we are not voting for Carney. We are voting for the Member of Parliament that we believe will best represent us in Ottawa. In my view, the Liberals have yet again overlooked the island thereby stoking our underlying sense of western alienation. None of their south island candidates inspire me to want to vote for them as I do not believe they will be strong advocates for our region. The Liberal south island candidates recently moved here from somewhere else in Canada. Two of their rookie candidates are already mired in scandal. In the case of Will Greaves, an unfortunate twitter post from March 2024 led Rabbi Meir Kaplan to write to Prime Minister Carney asking him to reconsider Mr. Greaves’ candidacy for his “public statements that echo classic antisemitic tropes”.
But here’s the dilemma. On Vancouver Island we are not voting for Carney. We are voting for the Member of Parliament that we believe will best represent us in Ottawa. In my view, the Liberals have yet again overlooked the island thereby stoking our underlying sense of western alienation. None of their south island candidates inspire me to want to vote for them as I do not believe they will be strong advocates for our region. The Liberal south island candidates recently moved here from somewhere else in Canada. Two of their rookie candidates are already mired in scandal. In the case of Will Greaves, an unfortunate twitter post from March 2024 led Rabbi Meir Kaplan to write to Prime Minister Carney asking him to reconsider Mr. Greaves’ candidacy for his “public statements that echo classic antisemitic tropes”.
Esquimalt-Saanich-Sooke Liberal candidate Stephanie McLean, on the other hand, who resigned from the Alberta legislature before completing her first term, has been called out by her own NDP colleagues for her musings about the ability of MLAs to advocate inside government caucus. I was surprised that the Liberals would think that a controversial former NDP MLA from Alberta would make a good candidate to run against Maja Tait, the present Mayor of Sooke, who I approached to run with the BC Greens in the 2017 provincial election. Maja has deep roots in the community and has has an exemplary record of public service in Sooke.
Friday, April 18, 2025, Victoria, British Columbia:
 Today I waited in line for over two hours to cast my vote for Elizabeth May in the riding of Saanich Gulf Islands. While it would have been easy for me to vote for Saanich Councillor and NDP candidate Colin Plant, who I have known for quite some time and who I believe exemplifies stellar leadership in governance, I was concerned that without Elizabeth in Ottawa, critical environmental issues will be swept under the rug during parliamentary debates.
Today I waited in line for over two hours to cast my vote for Elizabeth May in the riding of Saanich Gulf Islands. While it would have been easy for me to vote for Saanich Councillor and NDP candidate Colin Plant, who I have known for quite some time and who I believe exemplifies stellar leadership in governance, I was concerned that without Elizabeth in Ottawa, critical environmental issues will be swept under the rug during parliamentary debates.
Like many of you, I have heard the NDP ads on the radio or seen the signs stating that we vote NDP to stop the conservatives on Vancouver Island. I agree in principle, with two notable exceptions. The candidates I list below I have either worked with or know quite well. Were I to reside in their ridings, I would vote for them knowing that they would advocate for Vancouver Island interests in Ottawa.
And finally, I am a huge fan of minority governments and I do not trust the Federal Liberals to be given free range with a majority government. While I desperately want Mark Carney to be our Prime Minister, I think it would be prudent for Canadians to ensure that NDP, Green and perhaps Bloc incumbents are elected to keep them honest. The leader of the Federal Liberals may have changed, but I remain unconvinced that the party insiders and staffers have taken heed of the message that they were sent by Canadians.
Let’s not split the vote on Vancouver Island and instead consider supporting the following candidates to ensure Mark Carney and the Federal Liberals have a minority government where our voices are heard!
These are the candidates I believe will best represent us on Vancouver Island:
1) Laurel Collins – NDP – Victoria
2) Gord Johns – NDP – Courtenay-Alberni
3) Alistair MacGregor – NDP -Cowichan-Malahat-Sooke
4) Paul Manly Green – Nanaimo-Ladysmith
5) Elizabeth May – Green – Saanich- Gulf Islands
6) Maja Tait – NDP – Esquimalt-Sooke-Saanich
The Paris Agreement is in trouble: UNFCCC needs to ratchet up their climate efforts
Earlier this week I had an article published in The Conversation. As Facebook appears to be blocking reposting of Canadian news articles, I have reproduced a version of it below. This version includes more information and a video produced by, and reproduced with the permission of Myles Allen.
Expanded Version of The Conversation article
Negotiations at the 29th Conference of Parties (COP29) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are entering their second week after things got off to a rocky start.
Even before the event started, many were stunned that COP29 would again be hosted by a petro state. Just last year, COP28 was held in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, and this year it is Azerbaijan’s turn. Approximately 90 per cent of Azerbaijan’s exports are in the oil and gas sector.
The president of Azerbaijan, Ilham Aliyev, has described oil and gas resources as a “gift of god.” Meanwhile, the country’s deputy energy minister (and chief executive of COP29) has been caught on tape using the conference to advance oil investment deals.
What is the UNFCCC
The UNFCCC was established in 1992 and open for signature at the famous Earth Summit at United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held in Rio de Janeiro from June 3 to 14, 1992, where Canada signed. In total, 198 countries are now parties to the UNFCCC, which formally came into force March 21, 1994. Its main objective is:
“stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.”
To address this objective, parties to the UNFCCC adopted a legally binding international treaty, known at the Paris Agreement, at COP21 in Paris. The overarching goal of the Paris Agreement is:
“Holding the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, recognizing that this would significantly reduce the risks and impacts of climate change”.
How successful have international negotiations been?
Since the establishment of the UNFCCC, the globally-averaged atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration has increased 18% (from 356 to 421 ppm) and the globally-averaged methane concentration has increased 11% (from 1735 to 1922 ppb). During this time the 5-year average rate of carbon dioxide increase has almost doubled from 1.3 ppm/years in 1992 to 2.5 ppm/year in 2023.
 Over the period 1992-2023 the global mean temperature has risen 0.9°C, now sitting at 1.18°C above the 20th century average and rising at 0.23 °C/decade. And when all anthropogenic greenhouse gases are converted to their carbon dioxide equivalent, the atmospheric concentration is 534 ppm CO2e approaching twice the preindustrial value.
Over the period 1992-2023 the global mean temperature has risen 0.9°C, now sitting at 1.18°C above the 20th century average and rising at 0.23 °C/decade. And when all anthropogenic greenhouse gases are converted to their carbon dioxide equivalent, the atmospheric concentration is 534 ppm CO2e approaching twice the preindustrial value.
At the same time, and despite more than three decades of negotiations, 2023 was 1.48°C warmer than the 1850-1900 preindustrial average and its looking like 2024 will be even warmer, almost certainly surpassing the 1.5°C mark for the first time.
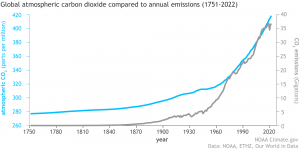 International negotiations have clearly failed to decrease anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions or stabilize global mean temperatures.
International negotiations have clearly failed to decrease anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions or stabilize global mean temperatures.
Neverthelss. the UAE Consensus, a landmark achievement of last year’s COP28, committed the parties to “transitioning away from all fossil fuels in energy systems, in a just, orderly and equitable manner in this critical decade to enable the world to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, in keeping with the science.”
This, however, begs an important question. Just what exactly does it mean to reach net-zero emissions “in keeping with the science?” I was a co-author in a recently published landmark study that may just help provide the answer.
What is net zero?
Defining net zero requires an understanding of timescales. Millions of years ago, trees, ferns and other plants were abundant when the atmosphere had much higher concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2).
 As the years went by, plants would grow and die. This dead vegetation would fall into swampy waters and, in time, turn into peat. Over millions of years, the peat turned into brown coal, then soft coal, and finally hard coal.
As the years went by, plants would grow and die. This dead vegetation would fall into swampy waters and, in time, turn into peat. Over millions of years, the peat turned into brown coal, then soft coal, and finally hard coal.
A similar process occurred within shallow seas where ocean plants (such as phytoplankton) and marine creatures would die and sink to the bottom to be buried in the sediments below.
Over millions of years, the sediments hardened to produce sedimentary rocks, and the resulting high pressures and temperatures caused the organic matter to transform slowly into oil or natural gas. The great oil and natural gas reserves of today formed in these ancient sedimentary basins.
Today, when we burn a fossil fuel, we are harvesting the sun’s energy stored in a life that lived millions of years ago. In burning fossil fuels, we release the carbon dioxide that had been drawn out of that ancient atmosphere — the same ancient atmosphere that had much higher levels of carbon dioxide than today.
Simply put, unless we can figure out a way to speed up the millions of years of geologic process, the idea that we can stop global warming solely through nature-based solutions or “planting a tree” simply isn’t realistic.
Reaching true net zero?
A series of scientific analyses published in 2007, February 2008, August 2008 and 2009 demonstrated that the stabilization of global mean temperatures required net-zero emissions. Policymakers interpreted these findings as a green light to emit carbon as long as these were natural “offsets.” This is a gross misinterpretation of the facts of net zero.
And so I, alongside a global team of 25 scholars and scientists involved in the early research, teamed up to correct this misinterpretation and explain just what exactly is (and is not) net zero.
Our research, recently published in Nature, makes four key recommendations for reaching true net zero:
- Stabilization of the global mean temperature at any level requires net-zero anthropogenic emissions;
- Reliance on “natural carbon sinks” like forests and oceans to offset ongoing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from fossil fuel use will not actually stop global warming;
- “Net zero” must be interpreted as “geological net zero” wherein each ton of carbon dioxide emissions released to the atmosphere through fossil fuel combustion is balanced by a ton of atmospheric carbon dioxide sequestered in geological storage;
- Governments and corporations are increasingly seeking carbon offset credit for the preservation of natural carbon sinks. Protection of natural sinks cannot be used to offset ongoing fossil fuel emissions if net zero is to halt warming;
Human activities since 1750 have emitted 2,634 billion tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere; 1,814 billion tons (69 per cent) of our total emissions originated from the combustion of fossil fuels and 820 billion tons (31 per cent) from changes in land use such as deforestation. As such, nature-based solutions only have a limited role to play in emissions reduction and certainly can’t be used to offset future emissions from fossil fuel combustion.
Nature-based solutions do, however, have an important role to play in climate change adaptation and the preservation of biodiversity, but there is a growing danger that governments, industry and the public will come to rely on them to maintain the status quo. This impulse must be avoided at all costs.
The example of British Columbia
The British Columbia New Democratic Party government has remained adamant that the province can reduce emissions to 40 per cent below 2007 levels by 2030. While admirable, there is a real risk that this target can only be achieved through creative carbon accounting and the use of natural sinks that will not stop warming.
 For example, Shell Canada is now promoting its efforts to ensure “the protection and restoration of natural ecosystems such as forests, grasslands and wetlands” as a central component to its greenhouse gas mitigation strategy.
For example, Shell Canada is now promoting its efforts to ensure “the protection and restoration of natural ecosystems such as forests, grasslands and wetlands” as a central component to its greenhouse gas mitigation strategy.
Of course, there is no mention of greenhouse gas emissions from the ever-increasing area burnt by Canadian wildfires. Nor does Shell mention the emissions being released as permafrost thaws and previously frozen organic matter begins to decompose.
The Darkwoods Forest Carbon project offers a glimpse into what is being considered by government and industry decision-makers as a means of offsetting emissions from the natural gas sector. The project aims to “offset” these emissions with carbon trading and forest conservation.
Such efforts will prove futile and, as we have shown, natural carbon sinks (like forests) do not stop warming and cannot be considered offsets.
Lesson for negotiators
As we move into the final week of COP29, one can only hope that international negotiators acknowledge the difference between natural and geological sinks of anthropogenic carbon.
Only the latter will lead to net-zero emissions and keep warming to below 3C above pre-industrial levels. Of course, the most efficient way to reduce emissions is to rapidly decarbonize global energy systems. Everything else only delays the inevitable.
Policy negotiations should be focused on eliminating emissions at source and developing approaches to directly extract and geologically store carbon dioxide already present in the atmosphere.
Sadly, given socioeconomic inertia, ongoing political inaction and geopolitical instability, as well as the slow rate at which energy systems are transforming to become emissions free, it is almost certain that 1.5C warming will be surpassed imminently with 2C following suit within the next two decades. The Paris Agreement is in trouble.
Surely we can do better.
To summarize
A rather direct summary translation of our recent paper can also be found in this satirical video. If you are offended by foul language, perhaps ski the video!
How can BC’s environmental organizations be more effective?
I’ve commented before that I’m thrilled with the outcome of the 2024 BC Provincial election that gave the BC NDP a razor thin majority. With 47 seats compared to 44 held by the BC Conservatives and two by the BC Greens, David Eby and the BC NDP have been sent a strong message. British Columbians have rejected ideological-driven activism, empty promises with destructive consequences, and out-of-touch hubris in favour of a more open, decentralized and inclusive approach to governance.
The BC Conservatives came within a hair of forming government and are now considered BC’s government in waiting. British Columbians were unsure what a BC Conservative government would look like and instead gave their numerous rookie MLAs valuable time to gain legislative experience while their nascent party infrastructure is strengthened and their policy platform more carefully constructed. And the electorate have rejected the far left ecosocialist agenda espoused by the now unelected BC Green leader in favour of a back to basics centrist approach.
But where does this leave BC’s environmental organizations? To be blunt, they’ve become largely inconsequential. The BC NDP don’t have to listen to them; the BC Greens will feel betrayed by them; the BC Conservatives feel like they are the enemy. That’s a recipe for irrelevancy, not influence. Please let me explain.
 Many within the environmental community campaigned against the Greens in 2017 out of fear of a BC Liberal majority. The tired “vote splitting” narrative was the central justification for not voting Green. Yet the BC Greens ended up holding the balance of power with 17% of the popular vote and 3 Green MLAs being elected. Our solutions-based message of viewing environmental challenges through the lens of the opportunity they present for innovation resonated with many centrist voters in rural and urban BC.
Many within the environmental community campaigned against the Greens in 2017 out of fear of a BC Liberal majority. The tired “vote splitting” narrative was the central justification for not voting Green. Yet the BC Greens ended up holding the balance of power with 17% of the popular vote and 3 Green MLAs being elected. Our solutions-based message of viewing environmental challenges through the lens of the opportunity they present for innovation resonated with many centrist voters in rural and urban BC.
Post 2017, many environmental organizations decided that the best strategy to advance their agenda would be to pressure the BC Greens in an attempt to influence the BC NDP indirectly. But their approach was ineffective as it was clear that many within the environmental community were perpetually stuck in combat mode. They didn’t seem to know how to:
- Offer pragmatic, constructive solutions;
- Recognize that perfection is the enemy of progress;
- Support decisions and decision makers once a decision has been made that they agree with;
- Work across partisan lines to build relationships and trust;
- Recognize that they are but one stakeholder in any policy discussion/deliberation and a diversity of voices must also be heard.
Organizing for Change, an umbrella organization, was particularly ineffective in this regard. I’ll never forget the day they sent a delegation to the legislature to lobby the BC Greens about minutia that I don’t recall. Yet just a week earlier — in their quest to do what the BC Liberals were unable to — the BC NDP introduced Bill 10, Income Tax Amendment Act 2019 embodying an intergenerational sellout to bring LNG to BC funded through a stunning package of corporate welfare. My two BC Green colleagues and I would have welcomed some external pressure from the environmental community on the BC NDP government. We spent hours speaking against the Act and proposed three amendments (Reasoned, Hoist and Send to Committee) designed to kill the bill. These were all defeated. Deafening silence was all that we heard from BC’s environment organizations.
| 2nd Reading & Reasoned Amendment (1:46:38) | Hoist Motion (43:12) | |
| Motion to Send to Committee (26:19) |
Even worse, the day that Organizing for Change were lobbying us was also the day that Bill 10 came up for debate at committee stage. Nobody in their delegation was even aware that this was happening as my BC Green colleagues and I voted against every section of the bill (including the title). And so, while the environmental activists were quietly watching from the public gallery, the BC NDP and BC Liberals were passing legislation that enabled the single biggest point source of greenhouse gas emissions in BC’s history.
But what saddened me the most that day was the fact that I knew full well that many BC NDP MLAs rose and supported this sellout as they were whipped into doing so. They voted against everything they apparently believed in. In fact, I sat in the legislature for 7 1/2 years and witnessed not a single instance when an NDP MLA voted against their party. This was not the case with the BC Liberals who had MLAs break ranks several times during my tenure in the legislature.
This is but one example that serves to illustrate why the BC environmental community has been wildly ineffective and has had very little impact in BC since 2017. The BC NDP don’t need to listen to them as they know that at the end of the day, the obviously partisan folk within this community will support them at the next election. As a result, the BC NDP can get away with patronizing and managing the environmental community. The BC Greens have likely learned their lesson that the pathway to success resides in a centrist, pragmatic approach to environmental policy. They cannot rely on the environmental community to support them (except in one or two ridings), and I suspect their leader is feeling particularly burned having watched the BC Green share of the popular vote cut by more than half (to 8%) from the 2017 high of 17%.
Meanwhile, the BC Conservatives will almost certainly ignore the BC environmental community. This is particularly ironic as the first seven letters of their party name are C-O-N-S-E-R-V. Yet it is perfectly understandable as the environmental community doesn’t appear to know how to be effective in their quest to advance environmental policy. Instead, it seems that they are stuck inside their own echo chamber calling people out without knowing how to call them in.
Some have criticized me for reaching out to John Rustad and the BC Conservatives during this past election. My response to them is to watch this video and compare it to what the BC Conservatives were saying just 6 months ago.
And the focus on food/water security & climate adaptation are not unrelated to John Rustad listening and modifying his earlier views based on the constructive dialogues we had. The environmental community in BC are ineffective as they too often demonize rather than attempt to build relationships and trust with decision makers. And I reiterate, the NDP don’t have to listen to them as they’ve shown their hand…they will support the NDP no matter what.
Had the BC Conservatives won a majority government, and they came very close to doing so, who would have been there to advise them on the challenges and opportunities associated with ongoing global warming. Many, if not most, of BC’s environmental organizations would have simply been shut out and ignored.
Consider this as wisdom from an elder in the climate community who has worked on the climate file since the late 1980s. Take it or leave it as you see fit. Many of today’s activists were not even born when I joined my climate science colleagues in raising public awareness of the challenges and opportunities associated with ongoing global warming. My concluding advice to those aspiring to facilitate environmental policy change in this province is to emphasize these points:
- Offer pragmatic, constructive solutions;
- Recognize that perfection is the enemy of progress;
- Support decisions and decision makers once a decision has been made that they agree with;
- Work across partisan lines to build relationships and trust;
- Recognize that you are but one stakeholder in any policy discussion/deliberation and a diversity of voices must also be heard.
You’ll be surprised at how much more effective you will be.
An exciting time in BC politics: Where do we go from here?
Elections BC has announced the initial 2024 BC Election results and I am absolutely thrilled to see how things played out on October 19. While recounts are scheduled for two ridings where the NDP presently lead by < 100 votes (Juan de Fuca-Malahat and Surrey Centre), and about 49,000 absentee and mail-in ballots have yet to be counted, the NDP hold a one seat lead with the BC Greens once more holding the balance of power.
Embedded within the election results are some very clear messages that party leaders should heed.
 First, neither the BC Conservatives nor the BC NDP received a majority suggesting:
First, neither the BC Conservatives nor the BC NDP received a majority suggesting:
- British Columbians no longer want to be guinea pigs in Eby’s tone deaf policy experiments. They want him to empower his cabinet, work hard to reach consensus with his cabinet colleagues and start listening to what regular folk are saying. Eby’s failure to obtain a majority was not unexpected. As I wrote in the Vancouver Sun on July 9, 2024:
Since assuming the premier’s chair in November 2022, radical ideological-driven activism, empty promises with destructive consequences, and out-of-touch hubris embody the hallmarks of his tenureBut British Columbians have given David Eby a second chance under the watchful eyes of the BC Greens.
- British Columbians did not trust the BC Conservatives enough for them to be given the keys to governance. The BC Conservatives had too many inexperienced candidates, too many candidates associated with odd conspiracy theories, and too much uncertainty surrounding them to be granted a majority. Yet British Columbians have put the BC NDP on notice that they need to do better. A strong BC Conservative caucus has emerged and that caucus will only get stronger as they gain more experience in the BC Legislature. The BC Conservatives will be eager to demonstrate why they are a government in waiting.
 Second, the BC Greens were also sent a very clear message. The ecosocialist, far left direction that the present leader has taken the party did not resonate with British Columbians. The BC Green popular vote was slashed in half from the 17% obtained in 2017, the last time the BC Greens held the balance of power. And the BC Green leader was easily beaten by the BC NDP candidate in the progressive riding of Victoria-Beacon Hill.
Second, the BC Greens were also sent a very clear message. The ecosocialist, far left direction that the present leader has taken the party did not resonate with British Columbians. The BC Green popular vote was slashed in half from the 17% obtained in 2017, the last time the BC Greens held the balance of power. And the BC Green leader was easily beaten by the BC NDP candidate in the progressive riding of Victoria-Beacon Hill.
 Yet two BC Greens got elected. These were in the ridings of West Vancouver-Sea to Sky and Saanich North and the Islands. West Vancouver-Sea to Sky (and its predecessor West Vancouver-Howe Sound) has been a BC Liberal stronghold since 1991; Saanich North and the Islands was another BC Liberal stronghold since 1991 (until Adam Olsen appeared on the scene in 2013). And I was first elected as a BC Green MLA in 2013 by unseating a BC Liberal cabinet minister who had represented the riding for 17 years.
Yet two BC Greens got elected. These were in the ridings of West Vancouver-Sea to Sky and Saanich North and the Islands. West Vancouver-Sea to Sky (and its predecessor West Vancouver-Howe Sound) has been a BC Liberal stronghold since 1991; Saanich North and the Islands was another BC Liberal stronghold since 1991 (until Adam Olsen appeared on the scene in 2013). And I was first elected as a BC Green MLA in 2013 by unseating a BC Liberal cabinet minister who had represented the riding for 17 years.
 If the BC Greens want to remain relevant, they have a very clear pathway forward. And that pathway involves repositioning the party as a viable centrist option that is fiscally conservative, socially progressive and environmentally responsible. But that can only happen with a new leader at the helm who can once more inspire the centrist voters back to the party.
If the BC Greens want to remain relevant, they have a very clear pathway forward. And that pathway involves repositioning the party as a viable centrist option that is fiscally conservative, socially progressive and environmentally responsible. But that can only happen with a new leader at the helm who can once more inspire the centrist voters back to the party.
What’s a voter to do? Vote for the party, the person or “None of the Above”?
With just over two weeks to go before the BC provincial election, we’ve entered the twilight zone of political campaigning. Political parties and their hyper partisan foot soldiers are hitting the streets, the airwaves and the internet with outrageous rhetoric, promises and accusations.
![]() The BC NDP have decided that incentivizing demand, a policy that will only drive up house prices and increase the debt burden for first time homebuyers, is somehow the way to deal with housing affordability. At the same time, and just two weeks after releasing the 2024/25 first quarter fiscal update projecting a whopping $9 billion deficit this year, they promised to give the average family a $1000 hand out. The BC NDP’s Dave Dollars giveaway mirrors the cynical Ralph Bucks that were doled out by Alberta’s Premier Ralph Klein starting in 2006.
The BC NDP have decided that incentivizing demand, a policy that will only drive up house prices and increase the debt burden for first time homebuyers, is somehow the way to deal with housing affordability. At the same time, and just two weeks after releasing the 2024/25 first quarter fiscal update projecting a whopping $9 billion deficit this year, they promised to give the average family a $1000 hand out. The BC NDP’s Dave Dollars giveaway mirrors the cynical Ralph Bucks that were doled out by Alberta’s Premier Ralph Klein starting in 2006.
 The BC NDP’s Dave Dollars announcement came just two days after the Conservative Party of BC touted their Rustad Rebate that would eventually exempt up to $3000 per month in rent or mortgage payments from provincial taxation. Existing landowners and homeowners are no doubt salivating as it gives renters and potential buyers more money to spend on rent and houses thereby pushing up prices due to an existing supply shortage. Not to be outdone with populist policy announcements, the Conservatives just released their Powering BC energy plan that ironically demonstrates energy illiteracy while proposing to “build trust and energy literacy” in British Columbia. The document demonstrates a profound lack of understanding of energy production, transmission and storage in British Columbia and reads like it was written by 20-something year old staffers imported from Premier Danielle Smith’s Alberta team.
The BC NDP’s Dave Dollars announcement came just two days after the Conservative Party of BC touted their Rustad Rebate that would eventually exempt up to $3000 per month in rent or mortgage payments from provincial taxation. Existing landowners and homeowners are no doubt salivating as it gives renters and potential buyers more money to spend on rent and houses thereby pushing up prices due to an existing supply shortage. Not to be outdone with populist policy announcements, the Conservatives just released their Powering BC energy plan that ironically demonstrates energy illiteracy while proposing to “build trust and energy literacy” in British Columbia. The document demonstrates a profound lack of understanding of energy production, transmission and storage in British Columbia and reads like it was written by 20-something year old staffers imported from Premier Danielle Smith’s Alberta team.
 To top it off, the BC Greens, lost in an ecosocialist hinterland, issued a platform that virtue signals a pathway to economic collapse. Their bizarre approach to deal with British Columbia’s housing shortage is to rage on the “for-profit industry that financializes” it. I’m not sure how musing about Marxist doctrine that “justifies and predicts the emergence of a stateless and classless society without private property” is helpful in increasing housing supply.
To top it off, the BC Greens, lost in an ecosocialist hinterland, issued a platform that virtue signals a pathway to economic collapse. Their bizarre approach to deal with British Columbia’s housing shortage is to rage on the “for-profit industry that financializes” it. I’m not sure how musing about Marxist doctrine that “justifies and predicts the emergence of a stateless and classless society without private property” is helpful in increasing housing supply.
 No political party has offered a vision that would inspire you to vote for them. Rather, the BC NDP are spending most of their time telling voters why they should be afraid of John Rustad and the BC Conservatives. The BC Conservatives are spending most of their time announcing what NDP policies they would undo. And not a day goes by without a BC Conservative candidate or their Leader, being associated with one batshit crazy conspiracy theory or another. Meanwhile the BC Greens, under their last-one-turn-out-the-lights sanctimonious leadership and dysfunctional organizational capacity, remain lost in the wilderness as they seek too inspire a handful of activists on the far left of the political spectrum.
No political party has offered a vision that would inspire you to vote for them. Rather, the BC NDP are spending most of their time telling voters why they should be afraid of John Rustad and the BC Conservatives. The BC Conservatives are spending most of their time announcing what NDP policies they would undo. And not a day goes by without a BC Conservative candidate or their Leader, being associated with one batshit crazy conspiracy theory or another. Meanwhile the BC Greens, under their last-one-turn-out-the-lights sanctimonious leadership and dysfunctional organizational capacity, remain lost in the wilderness as they seek too inspire a handful of activists on the far left of the political spectrum.
Sadly, my prediction for this election is that the winner will be the non voter. I wouldn’t be surprised to see a very low voter turnout and even perhaps record high numbers of spoiled ballots.
With that said, I have always voted for the local candidate who I believe would best represent the riding I live in. In the last four BC Elections I voted for Ida Chong (BC Liberal in 2009), myself (BC Green) in 2013 and again in 2017, Murray Rankin (BC NDP) in 2020 and I will vote for Stephen Andrew (BC Conservatives) in 2024. The choice would be hard for me in a number of other ridings where I might be tempted to write None of the Above on my ballot or where there are two candidates I might have to decide between. Kootenay Central comes to mind in the latter case as I have enormous respect for both Nicole Charlwood (BC Greens) rand Brittny Anderson (BC NDP).
In case anyone is interested, below is a list of twelve candidates (focusing on Vancouver Island) that I would certainly vote for if I lived in their riding. In the spirit of non partisanship, I offer three BC Conservative candidates, three former BC United Candidates who are now running as independents and six NDP candidates. I could write long essays as to why I support each of these people, but I will simply link you to their candidate pages so you can read up on them yourselves. There are others who I know or have worked with in other ridings, but I didn’t want to skew the non-partisan nature of my list.
I have an easy choice in Oak Bay Gordon Head where my long time friend Stephen Andrew is on the ballot. Coincidentally, when I announced my decision to run with the BC Green Party in Oak Bay Gordon Head on September 20, 2012, I did so on Stephen Andrew’s CFAX 1070 radio show!
Here’s the list:
| George Anderson | Nanaimo-Lantzville | BC NDP | |
| Stephen Andrew | Oak Bay-Gordon Head | BC Conservatives | |
| Mike Bernier | Peace River South | Incumbent | Independent (formerly BC United) |
| Gavin Dew | Kelowna-Mission | BC Conservatives | |
| Stephanie Higginson | Ladysmith-Oceanside | BC NDP | |
| Karin Kirkpatrick | West Vancouver-Capilano | Incumbent | Independent (formerly BC United) |
| Grace Lore | Victoria-Beacon Hill | Incumbent | BC NDP |
| Sheila Malcolmson | Nanaimo-Gabriola Island | Incumbent | BC NDP |
| Ravi Parmar | Langford-Highlands | Incumbent | BC NDP |
| Lana Popham | Saanich South | Incumbent | BC NDP |
| Tom Shypitka | Kootenay-Rockies | Incumbent | Independent (formerly BC United) |
| John Wilson | Esquimalt-Colwood | BC Conservatives |











